Trends in AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines, enabling them to perform tasks that typically require human cognition, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
AI is continuously evolving, with emerging technologies reshaping industries. Some of the latest trends include:
Explainable AI (XAI)
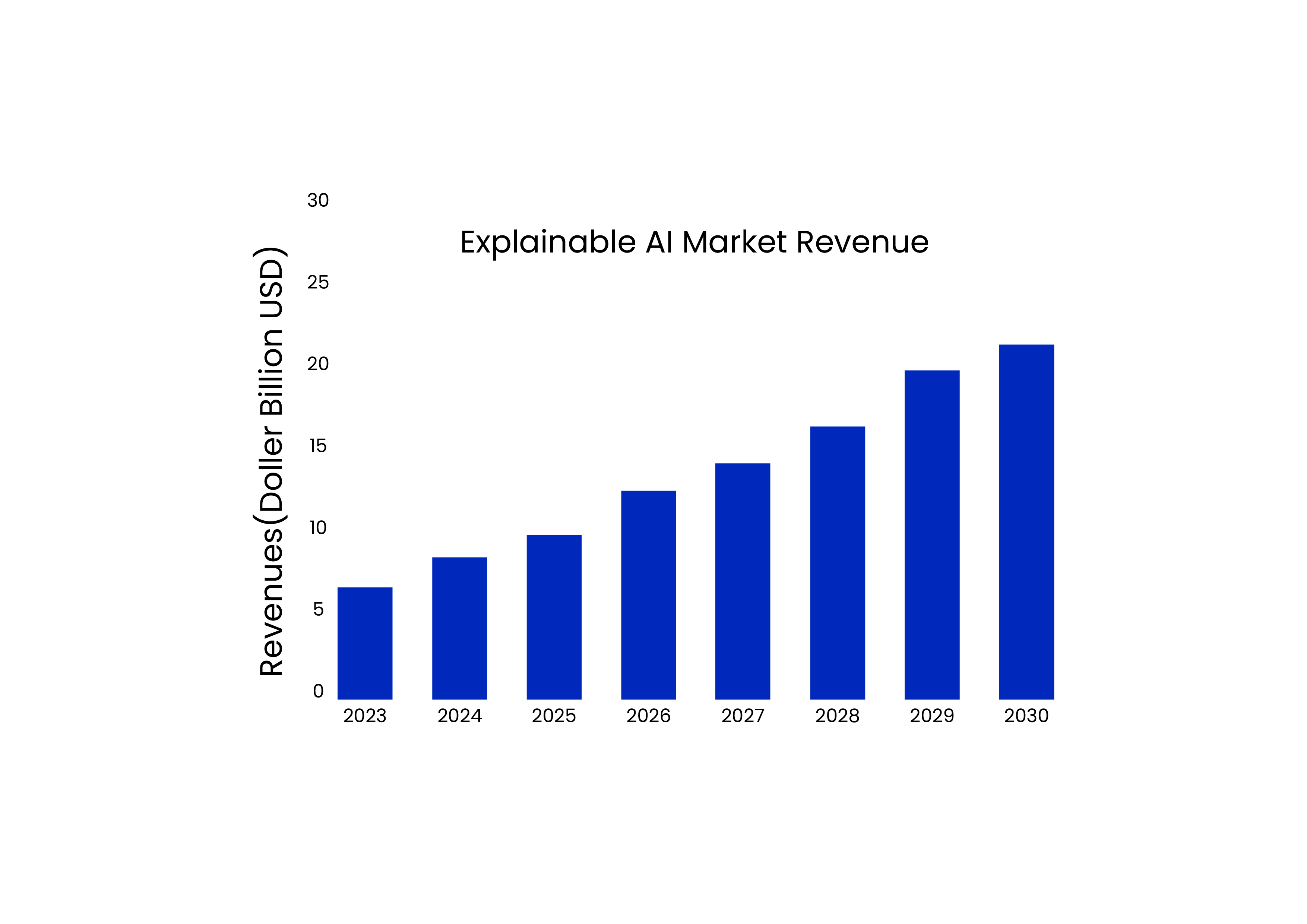
Explainable AI (XAI) enables human users to understand and explain the reasoning behind AI – generated decisions and predictions. It focuses on providing clear explanations for the outcomes. The size of the worldwide Explainable AI market was estimated at USD 6.68 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 21.3% from 2024 to 2030, reaching USD 24.58 billion.
Agentic AI
Agentic AI can make decisions and act independently. It can adapt to new information, learn, and improve over time.
How does agentic AI work?
Agentic AI systems use multiple AI agents that can analyze data, set goals, and take actions.
It can collaborate with humans to solve problems.
Agentic AI can learn from its environment and adjust its actions accordingly.
It can also adapt to changing environments and events.
Few examples of Agentic AI
Supply chain management
Agentic AI can automatically adjust delivery routes and schedules based on traffic conditions and shipment priorities.
HR
Agentic AI can automate complex tasks, allowing employees to focus on high-impact decisions.
Customer Service
AI agents may assist human employees in “getting the answer quicker and serving the customer quicker,”. AI agents’ function as a helper tool can assist in making sure that all employees, skilled or unskilled, and experienced or inexperienced, offer a high standard of service to customers consistently.
AI in Different fields
Banking and Finance
Banking uses AI to improve client experiences, security, and efficiency. With repetitive tasks such as fraud detection and data entry automated, it reduces operating costs. Chatbots powered by AI offer round-the-clock client service. Customer data is analyzed by machine learning algorithms to improve security by detecting anomalous transactions and personalizing services.
The main ways that banks may utilize AI effectively:
Anticipating and spotting risk and fraud,
Finding new business opportunities,
Optimizing operations, and tailoring services and products to individual needs.
Healthcare
AI-powered diagnostic tools, robotic surgeries, and virtual health assistants are improving patient care. AI is also used for drug discovery, medical imaging analysis, and personalized treatment plans.
Machine Learning in Healthcare enhances diagnosis, treatment, and cost efficiency by analyzing clinical data. Deep learning aids in speech recognition.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) improves diagnosis accuracy, streamlines clinical workflows, and personalized patient care. It extracts insights from medical records and helps manage complex health data.
Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) provides evidence-based insights for better medical decisions. It ensures timely, data-driven interventions via EHRs, mobile devices, and dashboards.
Using Agentic AI can collect real-time data from patients on medication usage and outside factors like air quality in smart inhalers.
Cybersecurity
AI-driven security systems detect and neutralize cyber threats in real-time. Machine learning models analyze vast amounts of data to identify unusual activities and prevent cyberattacks.
In 2020, there was a cyberattack on the central server of the National Highway Authorities of India (NHAI) due to weak cybersecurity infrastructure. Using EXAI can provide insights into why such incidents happen and what steps could be taken to avoid such cyber attacks.
Fast and Accurate Threat Detection: AI rapidly analyzes vast data to detect anomalies and identify risks, ensuring quicker threat response.
Automation of Security Tasks: AI automates log analysis and vulnerability scanning, allowing security teams to focus on critical strategies.
Predictive Threat Analysis: AI identifies attack patterns to anticipate future threats, helping organizations stay ahead of cybercriminals.
Defense and Military Applications
AI is assisting in drone surveillance, autonomous weapons, predictive maintenance for military equipment, and battlefield analysis, increasing efficiency and strategic decision-making.
AI for Border Surveillance
AI-powered cameras, sensors, and radar enhance border intrusion detection, target classification, and defense operations.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
AI-driven drones enable day-and-night reconnaissance and surveillance, improving border control efficiency.
Lethal Autonomous Weapon Systems (LAWS)
AI-equipped weapons autonomously track and engage hostile targets, reducing personnel needs.
Autonomous Vehicles & Robots
Unmanned armored vehicles and robots excel in monitoring, casualty evacuation, and operations in difficult terrains.
Data Management & ISR
AI processes underused data to enhance Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) capabilities.
Pattern Identification
AI analyzes multiple data sources to predict and pre-empt terrorist or insurgent threats.
Training & Simulation
AI-based simulations support military training, offering models for various combat systems and real-world scenarios.
How AI is shaping the future
AI has found applications across various fields, including:
Smart Assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant)
Autonomous Vehicles (e.g., Tesla, Waymo)
Facial Recognition (used in security and authentication)
Robotics (used in manufacturing, healthcare, and space exploration)
AI-powered Customer Service (chatbots and virtual assistants)
AI in Agriculture (crop monitoring, yield prediction, and automated farming)
AI in Marketing (targeted advertising, data analysis, and customer insights)
Benefits of AI
Efficiency and Automation: AI automates repetitive tasks, increasing productivity and reducing human error.
Enhanced Decision-Making: AI processes large datasets quickly to provide insights for informed decision-making.
Cost Reduction: AI-driven automation minimizes operational costs and maximizes efficiency.
Improved Accuracy: AI-powered systems, such as in healthcare and finance, provide accurate analysis and predictions.
Personalization: AI tailors user experiences in e-commerce, entertainment, and education.
Continuous Learning: AI models improve over time by analyzing new data and adapting to changing trends.
Risks of AI
Job Displacement: AI automation may replace human jobs, particularly in industries reliant on repetitive tasks.
Ethical Concerns: AI decision-making can be biased if not properly trained, leading to discrimination and unfair outcomes.
Security Threats: AI can be exploited for cyberattacks, deepfake creation, and malicious activities.
Loss of Human Control: Over Reliance on AI in critical systems may lead to unforeseen failures and vulnerabilities.
Privacy Issues: AI-driven data collection can lead to breaches of personal privacy and misuse of information.
Weaponization of AI: Autonomous weapons and AI-driven warfare raise concerns about global security and ethical implications.
Risk Mitigation Strategies for AI Implementation
Addressing Job Displacement: Implementing reskilling and upskilling programs to help workers transition to new roles. Promoting human-AI collaboration rather than full automation.
Mitigating Ethical Concerns: Developing and enforcing AI ethics guidelines to prevent bias in decision-making. Ensure diverse and representative datasets for training AI models.
Strengthening Security Measures: Implementing robust cybersecurity protocols to protect AI from exploitation.
Maintaining Human Control Over AI: Designing AI with human-in-the-loop systems for critical decision-making.
Enhancing Privacy Protection: Implementing strict data encryption and anonymization techniques. Strengthening data protection laws and user consent mechanisms.